Relay is a protecting device which detects any kind of abnormal happenings(fault) in power system or in power system elements (like transformer, generator etc.) and sends a signal to circuit breaker to isolate the fault or to the alarm circuit to raise an alarm.
RELAY
IDENTIFICATION:
51- Over current
IDMT relay
51N-IDMT earth
fault relay
50-Over current
definite time relay
50N-Definite
time earth fault relay
49-Thermal
overload relay
46-Negetive
sequence relay
48-Motor
starting supervision
66-Restart inhibit
for motor
27-Under voltage
relay
87-Differential
relay
IDMT stands for Inverse Definite Minimum Time relay
SETTING
METHODS:
51
& 51N
51 and 51N are both inverse time relay and
used to detect phase fault and earth fault respectively. There setting methods
are same but the only difference is that pick up of 51 is higher than that of
51N.
Please check our article CT connection to sense earth fault/Earth Faults Detection Philosophy to know earth fault is detected.
Please check our article CT connection to sense earth fault/Earth Faults Detection Philosophy to know earth fault is detected.
The following parameters are required to
calculate the settings of 51 and 51N.
a. PICK UP: this is the value of current through relay for which the relay
picks up.
b. PSM (Plug Setting
Multiplier): this is the ratio of fault current
through relay coil and pick up current. (it is relays inherent property)
c. TSM (Time Setting
Multiplier): it is the ratio of required relay
operating time and actual relay operating time.
Basically if the TSM=1 then
the relay operating time is very high, that’s why a fraction given as TSM to
decrease the relay operating time as per requirement or to co-ordinate with the
up and downstream feeders.
Sample
calculation:
Pick
Up Calculation:
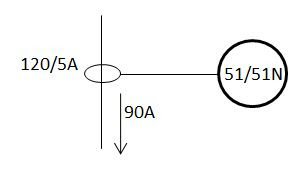 |
| Fig 1: IDMT relay setting/ https://electricaltechnologyrishi.blogspot.com |
The single diagram shows a very simple and
typical line, through which 90A current is flowing, a CT of rating 120/5A is connected
via which the 51 and 51N relays are connected.
Let say, the relay 51 will pick up for 120%
of full load current.
So current seen by the relay will be,
=120% X FLC
X CT Sec. /CT primary
=1.2 X 90 X
5/120
=4.5 A
So pick up setting or pick-up current of
the relay is 4.5 Amp.
Now remember one thing, that some relay
manufacturers make their relay pick up range in the following manner, say 0.5-10 X CT sec. That means the CT
secondary will be multiplied within the relay program. So here multiplication
with CT secondary will not be applicable.
For this type of relay the pick-up will be
=1.2 X 90/120=0.9
Relay
will display the following setting- 0.9 X CT sec (In) (In general In is referred as the relay rated current, which is in general same as the CT secondary current. That is CT secondary and Relay rated current shall be same. However there is exception for earth fault relay, which is beyond scope of this article)
So, it is strictly required to read the
relay catalogue and know the setting range.
Method of calculating pick up of 51N is
same as mentioned above, but the pick-up is considered as 5-10% of full load
current, if the feeder is being fed from a transformer which has NGR then
pick-up may be considered as 5-10% of NGR rating.
Suppose a transformer has an NGR of 400A for 10 sec i.e. limiting earth fault current upto 400 A. with NCT having ratio of 200/1A.
Then pick-up will be set as
=10% X 400 X CT sec/CT prim.
Here also see the relay catalogue to know
if the CT sec is required to be multiplied or it will be multiplied internally.
Following the above mentioned process pick
up of inverse time over current and earth fault relay is calculated.
However for earth fault protection is better to select minimum available pick up to ensure maximum sensitivity.
PSM
calculation:
PSM=Fault
current in relay coil/pick up current through the relay coil.
= (Fault Current X CT secondary/CT
primary)/ Pick up current through the relay coil.
Suppose fault
current is 1000A.
So, PSM will be
= ((1000X5)/120)/4.5
=41.66/4.5
=9.26
There are several
types of IDMT relay characteristics available now, according to the
characteristics the relay operating time are the determined. The formulas are as
follows:
 |
| Fig 2: IEC relay characteristics/ https://electricaltechnologyrishi.blogspot.com |
Ir the PSM value which has been calculated earlier.
Now,
Suppose we have to operate the relay at 0.75 sec (say).
So, TMS will be (for
standard inverse curve)= 0.75X((9.260^0.02)-1)/0.14
=0.24
So settings are –
1. Pick up= 4.5 or 0.9 X In(it will be according to the relay)
2. TMS=0.24
1. Pick up= 4.5 or 0.9 X In(it will be according to the relay)
2. TMS=0.24
Some typical settings-
PHASE FAULT
1. B/C AND I/C OF MCC: 80% OF THE BUSBAR RATING OR
120% OF THE CONNECTED LOAD (TAKE THE AVAILABLE DATA).
2. UPSTREAM RELAY OF SL NO. 1 ( i.e. O/G OF PCC):
SELECT PICK UP HIGHER THAN SELECTED FOR SL NO. 1
3. B/C AND I/C OF PCC: 120% OF TRANSFORMER FULL LOAD
CURRENT.
4. AT THE H.V SIDE OF THE TRANSFORMER (51 which is
back up of the downstream or LV side 51 relay): 130% OF TRANSFORMER HV SIDE
FULL LOAD CURRENT.
GROUND FAULT
1. B/C AND I/ OF MCC: 15-30% OF BUSBAR RATING.
2. UPSTREAM RELAY (O/G OF PCC):30% OF BUS BAR RATING
3. B/C AND I/C OF PCC: 20% OF TRANSFORMER FULL LOAD
CURRENT.
For 51N always use minimum available setting, that
will ensure maximum percentage of protection.
TIME GAP
TRY TO MAINTAIN
TIME GAP OF 0.25 SEC BETWEEN RELAYS.
50
& 50N
These can be used as definite time relay or
instantaneous relay.
For relay 50 connected at H.V side of the transformer: For such connection the pickup shall be more than the inrush current of the transformer. Otherwise the relay will trip during transformer starting.
Inrush current is generally 10-15 times of
transformer FLC.
 |
| Fig 3: Instantaneous relay setting/ https://electricaltechnologyrishi.blogspot.com |
Say transformer
H.T FLC is 90 A.
Then inrush will
be 10x90=900 A. we set pick up of the relay as 910 A.
So setting
is=910x5/120=37.9 A or (910/120) X In=7.58 X In as per the available Relay
functions.
Here also consider the relay catalogue as mentioned earlier.
If the 50 relay is connected with motor feeder for motor protection then pickup will be higher than the starting current of the motor.
Time delay may be
or may not be given depending upon the requirement of instantaneous or time
delayed operation.
50N setting
method is also same, but use minimum pick up setting, generally 5-10% of NGR
rating can be used. If NGR is not there then the same % of FLC can be used, but
try to use minimum pick up setting for the relay to ensure maximum percentage
of protection.
Hope you have enjoyed this article. Please share your opinion in the comment box. And for all of our other posts please visit the page "Site Map"
Thank you.......




Great
ReplyDeleteSupar sir
ReplyDeletecreative and amazing Article
ReplyDeletetechnology guest post
Very nice information.
ReplyDeleteRead More Article
TankPro series submersible Level sensor are manufactured for trouble free long life service in the both heavy and light industries. Able to measure the height of liquid above the position in the tank referenced to atmospheric pressure. The level sensor backlit LCD display for reading the level. Suitable for wastewater and slurry applications with features to protect the unit from these demanding applications. More details about Submersible Level Sensor
ReplyDeleteHello Sir, I have a question
ReplyDelete1. B/C AND I/C OF MCC: 80% OF THE BUSBAR RATING OR 120% OF THE CONNECTED LOAD (TAKE THE AVAILABLE DATA).--->> my question what is B/C and I/C?
2. UPSTREAM RELAY OF SL NO. 1 ( i.e. O/G OF PCC): SELECT PICK UP HIGHER THAN SELECTED FOR SL NO. 1 ---->> what you mean by O/G of PCC??
ReplyDeleteHello there, this is amazing blog i really appriciated. thats great you are good writer
Click here
Click here
Click here
Click here
Click here
Click here
Click here
Click here
Thank you
I have browsed most of your posts. This post is probably where I got the most Fault Location Services George Mason
ReplyDeletewhat you mean by B/C AND I/C and PCC, what does it stands for?
ReplyDeleteThank you sir...
ReplyDeleteThank you..
ReplyDeleteGreat Sir !!
ReplyDelete